Liquid Gas, including LPG – The Alternative Marine Fuel Towards 2050 By Nikos Xydas, Technical Director, WLGA

The IMO GHG strategy towards a net-zero GHG emissions world by 2050 continues its trajectory. As the global push for environmental sustainability continuously intensifies, Liquid Gas, particularly LPG, has a major role to play as an alternative marine fuel. The benefits of LPG have already been demonstrated through its wide adoption as the most common alternative fuel for LPG carriers. More than 285 LPG powered vessels have been ordered, and more than 155 of those are already on water, demonstrating the clear benefits of LPG.
The shipping industry has embarked on a decarbonisation pathway towards 2050 and beyond, and this is also the case for the Liquid Gas industry. As a fuel, LPG is a unique exceptional energy. The transportation, storage, and use of LPG have been established over several decades, while supply and supply chain infrastructure are widespread all around the world.
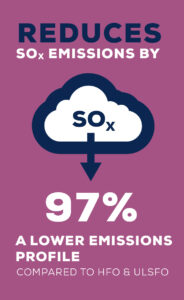
The combustion of LPG results in significantly lower emissions of sulphur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter compared to conventional marine fuels. LPG also offers a substantial reduction in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to heavy-fuel oil and this without any methane slip issues, as is the case with LNG, the other very credible alternative fuel for the shipping industry. LPG is one of the fuels that can help ship operators comply with the IMO GHG, strategy and the FuelEU for at least the next ten years.
From January 2025, the EU's FuelEU regulation requires a 2% cut, compared with 2020 base year levels, in the lifecycle greenhouse intensity for bunker fuels burnt in EU territorial waters. At this carbon intensity level, LPG is compliant up to 2035 with FuelEU's GHG limit set at 85.69 gCO₂e/MJ, similar to LNG, but in fact with even lower WtW carbon intensity. In reality, LPG offers the lowest carbon intensity than any other non-bio, non-renewable alternative marine fuel as demonstrated below.

The LPG powered vessels that have been ordered, currently over 285, and with many of them already operating, are clearly demonstrating the advantages of LPG as a fuel, saving more than two million tonnes of CO2 emissions annually, and paving the way to establish LPG as a crucial player in the quest for greener shipping. The consumption of the LPG fuelled vessels is estimated at one million tons by 2026. It is anticipated that 98% of all LPG very large gas carriers (VLGCs) that enter the market in the coming years will be capable of using LPG as a fuel.
Importantly, LPG is also seen by shipowners as one of the least expensive fuels for meeting the new low-carbon emission rules. In 2024, according to Argus media, it was shown to be very price-competitive compared to LNG, at same or lower cost than LNG. This is particularly important considering in addition, the known, lower CAPEX requirements of LPG. Indeed, LPG offers both attractive OPEX and CAPEX advantages compared to other alternatives.

For LPG however, in order to get to the top of the list that it deserves, in the bunker fuel options, the industry still needs to address bunkering infrastructure and availability of four-stroke engines.
In addition to the advantages of conventional Liquid Gas, and conventional LPG, the renewable alternatives can deliver an even lower-emissions marine transport fuel providing pathways toward future zero-carbon solutions. Moving simply from conventional Liquid Gas to renewable Liquid Gas as a drop-in fuel is a simple decarbonisation pathway for those already using the conventional fuel today or in the future. Clearly, conventional Liquid Gas, presents a cleaner pathway today, while renewable Liquid Gas, renewable LPG (rLPG) and renewable dimethyl-ether (rDME) provide a clear future-proof solution.
LPG is an ideal fuel for all types of vessels, from the largest VLGCs and container ships, to commercial fishing boats, recreational vessels and the smallest outboard motors. It is a fuel that exists everywhere today, it delivers its globally recognised benefits in all types of applications, and can clearly play a major role in the decarbonisation of the shipping industry.
Nikos Director,
WLGA Technical Director
About Liquid Gas, including LPG, as a Marine Fuel
LPG/Propane, is increasingly being used in marine engines in various types and sizes of vessels, from small leisure crafts with outboard engines, to fishing boats, patrol boats and larger vessels. It is an efficient marine fuel, it reduces exhaust emissions and eliminates the risk of fuels spills on the water. All information related to LPG as a Marine Fuel can be found on this page: Marine - WLGA